Bug Life Cycle in software testing is the specific set of states that defect or bug goes through in its entire life.
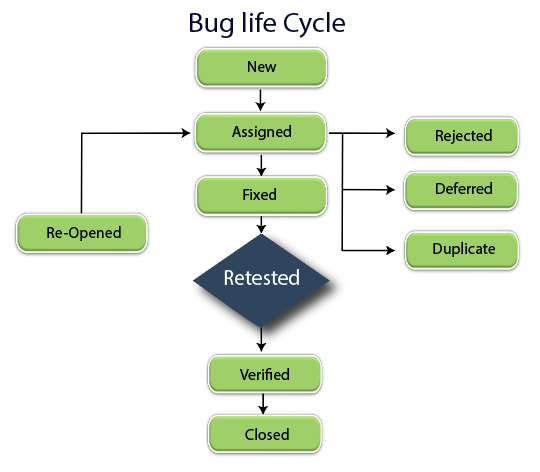
New: When a new defect is logged and posted for the first time. It is assigned a status as NEW.
Assigned: Once the bug is posted by the tester, the lead of the tester approves the bug and assigns the bug to the developer team
Open: The developer starts analyzing and works on the defect fix.
The bug or defect can be opened in three stages:
- Duplicate: If the defect is repeated twice or the defect corresponds to the same concept of the previous bug, then it changes the status to Duplicate.
- Rejected: If the developer feels that the defect is not a genuine defect, then it changes the status to Rejected.
- Deferred: If the bug is not of higher priority and can be solved in the next release, then the status changes to Deferred. The deferred state is also known as postpone state
Fixed: When a developer makes a necessary code change and verifies the change, he or she can make bug status as “Fixed.”
Retest: Once the bug is fixed by the software developers then it is assigned back to the testing team to check whether the bug has been fixed or not.
Reopen: If the bug persists even after the developer has fixed the bug, the tester changes the status to “reopened”. Once again the bug goes through the life cycle.
Verified: The tester retests the bug after it got fixed by the developer if no bug found then it changes the status to Verified
Closed: If the bug is no longer exists, then it changes the status to Closed.